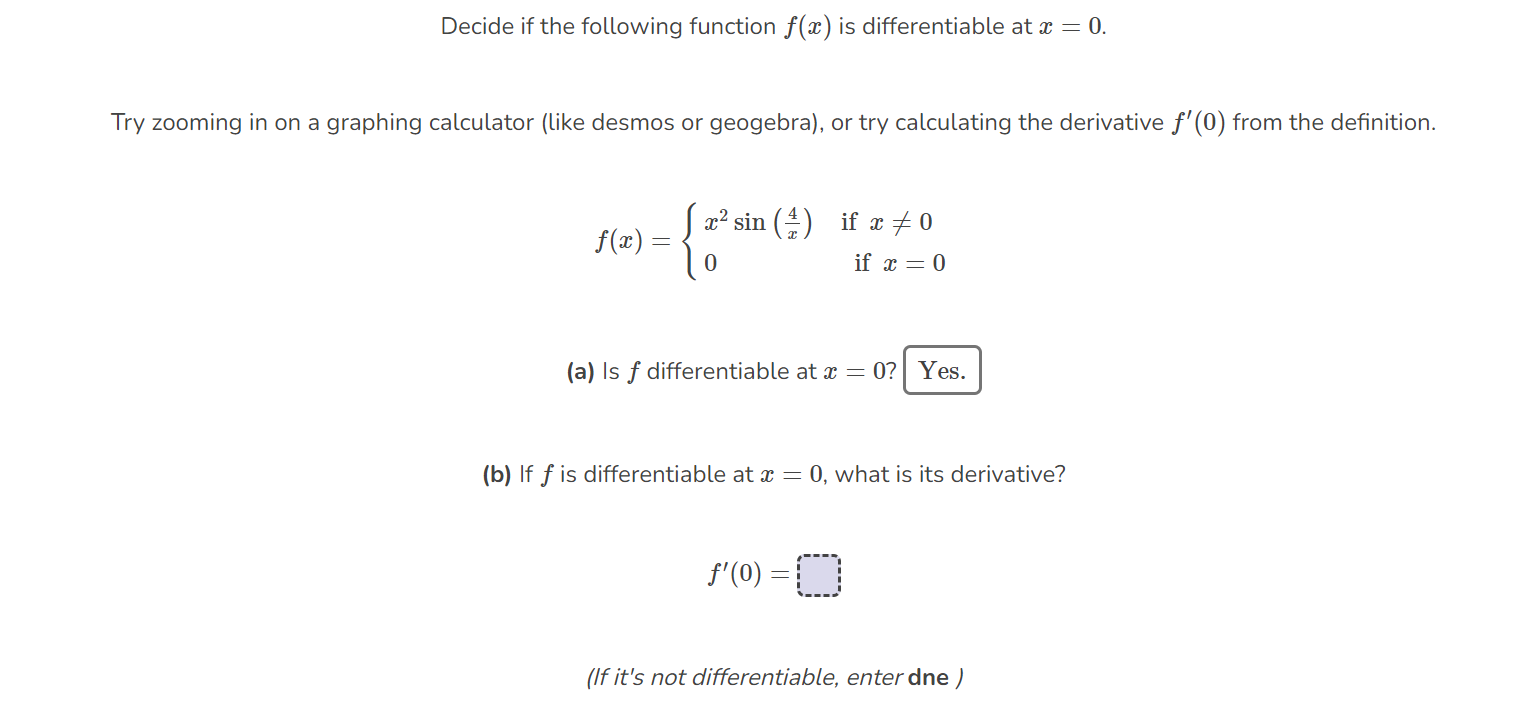
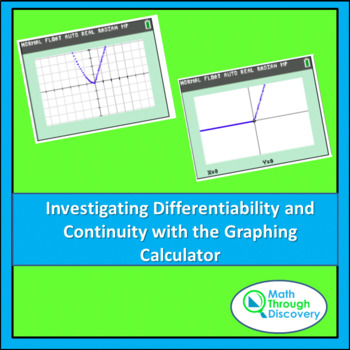
SOLVED: Decide if the following function f(x) is differentiable at x=0. Try zooming in on a graphing calculator (like desmos or geogebra), or try calculating the derivative f^'(0) from the definition. f(x)={

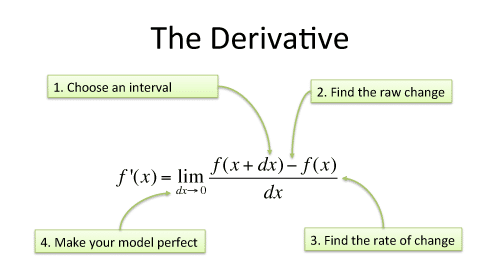
To be differentiable, a function must be continuous and smooth. Derivatives will fail to exist at: cornercusp vertical tangent discontinuity. - ppt download









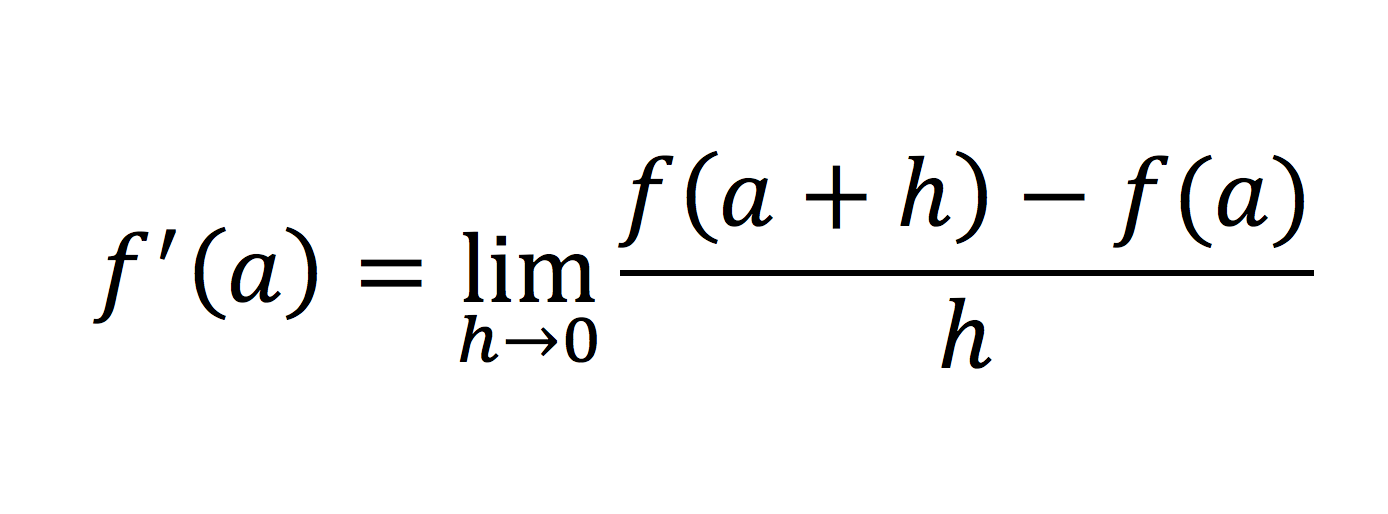

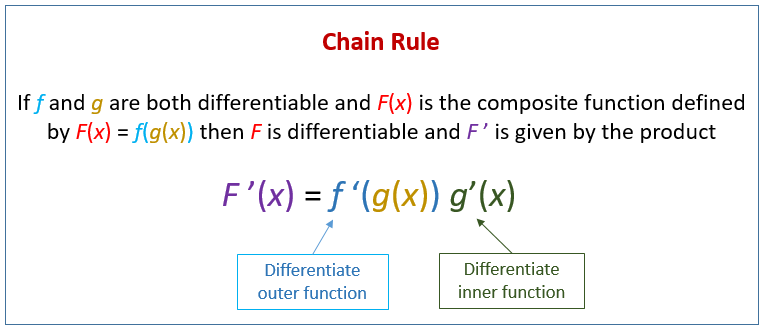
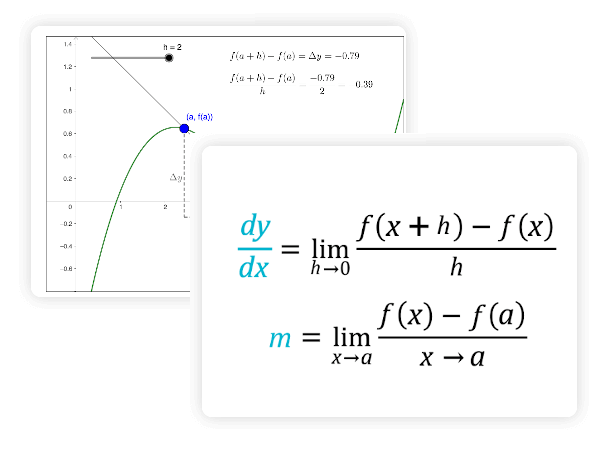

![AP Calculus] Using a calculator to take the derivative : r/HomeworkHelp AP Calculus] Using a calculator to take the derivative : r/HomeworkHelp](https://preview.redd.it/ap-calculus-using-a-calculator-to-take-the-derivative-v0-93ooh01wm74c1.png?auto=webp&s=45d189ce8293ec852aabfe7678611e8ee31a5eae)

